Published by
BluePi
Data-Driven Business Transformation
Forecast new product success scientifically
A new product is launched in the market to reduce the inflation cost of production by making improvements on existing products, targeted to the current market needs. New products are launched by introducing area-specific changes to extend the market space. New Products permit organizations to develop incomes and hold high edges by making new clients in new markets. More up to date products normally order higher margins in the market while more seasoned items are affected by serious difficulties and winding down client intrigue.
Organizations present new products that dislodge one of its own more established products known as Market Cannibalization. The cannibalization of existing products leads to no increase in the company’s market share despite sales growth for the new Product. Market cannibalization can occur when a new product is similar to an existing product, and both share the same customer base. Cannibalization can likewise happen when a chain store loses clients because of another store of a similar brand opening close by. Organizations regularly make updates in their product catalogue by adding new products to enter high-growth markets and to defend against competitions. Organizations are progressively subject to incomes from New Products to drive their top lines every year. Organizations need New Products to supplant existing items that are arriving at end-of-life. Profit is just one reason for presenting new products. Now and again, a firm will present an item that has a genuinely restricted budgetary return, yet it is essential to the firm in the general system will position in the commercial centre.
Need for Forecasting
Eliminating an unprofitable product is a useful reason to forecast as introducing a successful product. Demand forecasting is the process of predicting future sales by using historical data to make informed business decisions about everything from inventory planning, and warehousing needs to running promotions and meeting customer expectations. Demand forecasting helps the business estimate the total sales and revenue for a future period of time.
Forecasting can be difficult for new products as traditional time series forecasting methods based on historical data are not applied here due to very less or no historical data. However, new products introduced by an organization are not prominently new, rather new items are somewhat comparative items to the subset of results of an association. Having historical data of these similar products, an organization can leverage this information to generate forecasts for new products. There might be products with low similarity as well as high similarity having different Product Lifecycle. Forecasting Product Lifecycle can be implemented in case of new products as I have discussed further in the blog.
What is Product Lifecycle?**
The Product Lifecycle (PLC) depicts the stages of a product from launch to being suspended. It is an instrument that assists organizations in planning for new product development and refining existing products
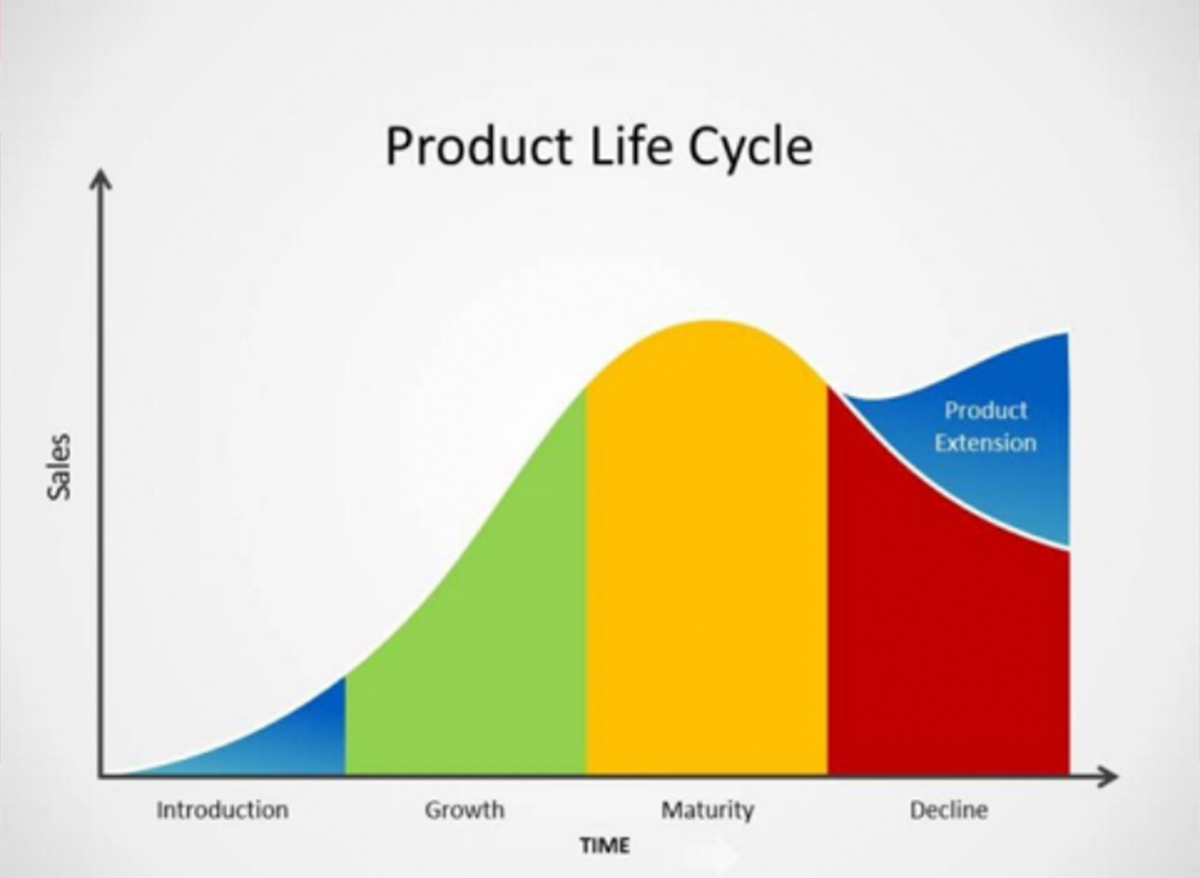
Stages of Product Lifecycle
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Decline
Growth Stage – In the Growth Stage, product popularity is increasing, and the product concept is proven.
Maturity Stage – At this stage, the competition has been increased, and there might befall in the demand of the Product making market saturated.
Decline Stage – In the decline stage, product demand drops significantly, and there is less demand for the Product. Most of the products have a declining stage, but some products prolong their Maturity Stage stay afloat for a longer time period.
How can we measure the success of new products?
The majority of the new products launched have 4 stages of the lifecycle: an introduction, an increase in demand, a stable stage in which the Product is considered “mature,” and finally decline. Our goal is to find the curve which fits the sales of the Product but not replicates it. These curves resemble triangles and trapezoids.
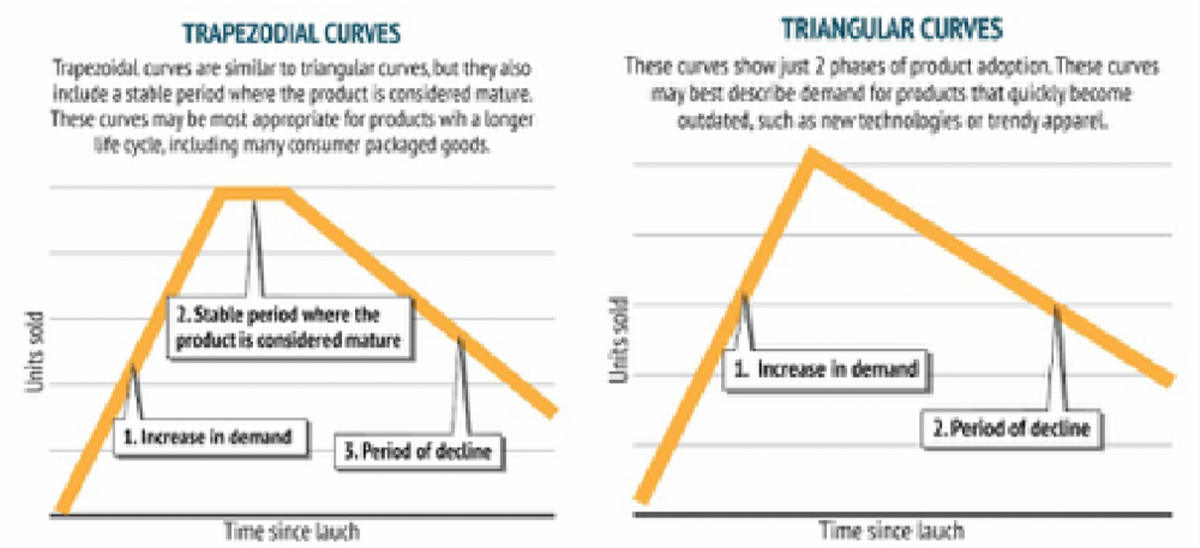
To measure the success of new products, we need to estimate three numbers: how long a product will sell for when the peak sales will occur, and how high the peak will be. We can do this by forecasting the Product’s life cycle. Getting an idea of the life cycle of the new Product, we estimate the demand which will help in defining the success of the Product.
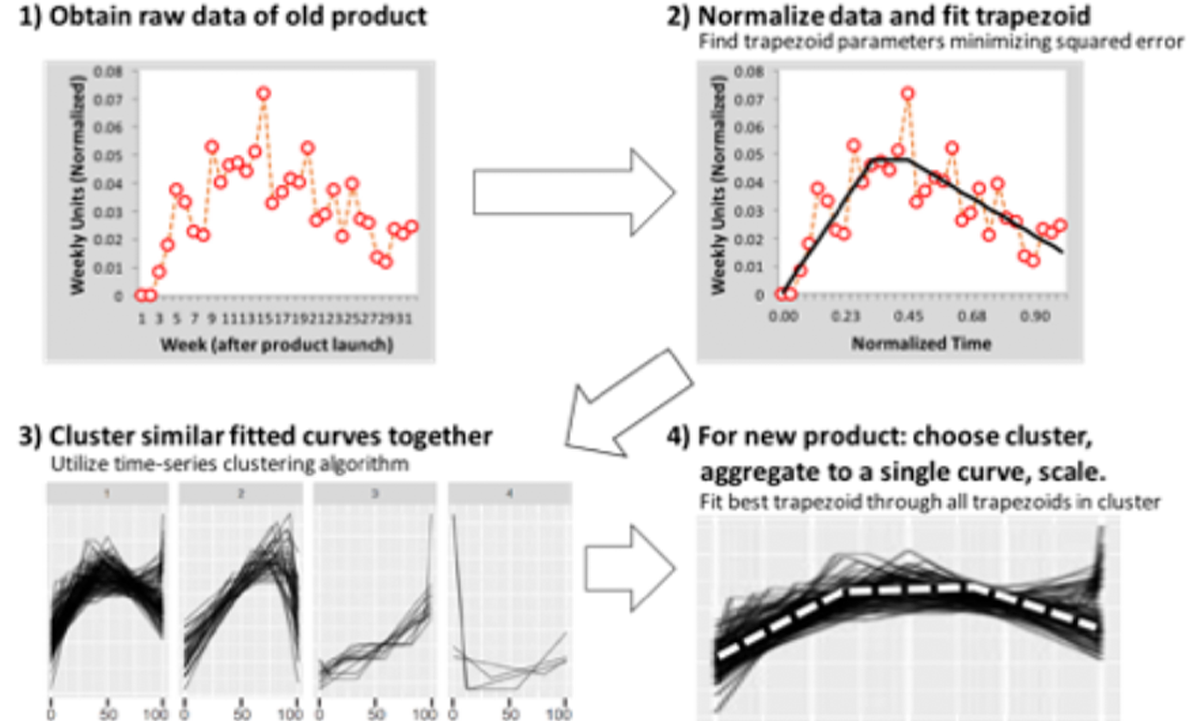
Steps to generate Product’s life cycle curve forecast
- Normalize and clean the historical data of all the products in the database such that total time length and the sum total of demand of products are equal to one which will help us to compare product life cycle curves having different lengths and volumes.
- Now for each Product normalized historical demand, a curve is fit through the data. After fitting the life cycle curves through each old Product’s data, these fitted curves are clustered together into distinct groups. As a result, we get a set of clusters, each of which has a subset of the products whose product life cycle shapes are similar to each other.
- MaturityNow we will find the cluster, which contains products similar to the new Product. The product life cycle curves within this cluster are aggregated into a single normalized product life cycle curve. Then, this curve is scaled to be the length of the new Product’s life cycle.
Conclusion
Using the forecasted life cycle curve, we can estimate the weekly demands for new products and compare the results with the demand needed to generate profit for an organization and to measure the success of new products